Buckling Analysis of a Tank
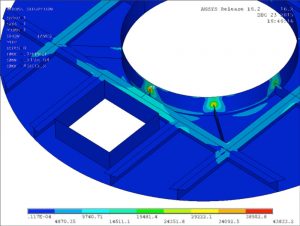
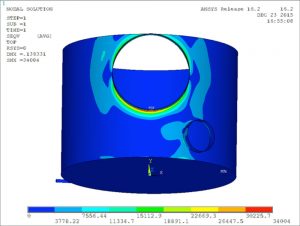
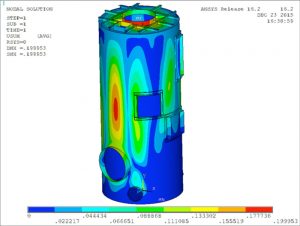
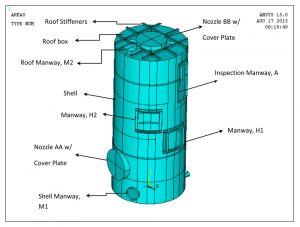
The scope of this analysis was to perform buckling analysis on a tank under the external operating pressure. Stiffening rings were added to the outside of the shell and the head to eliminate the buckling.
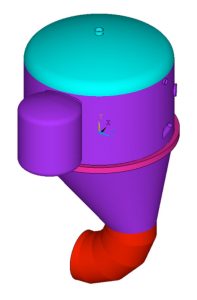
- General Layout for the Tank Without Added Stiffening Rings
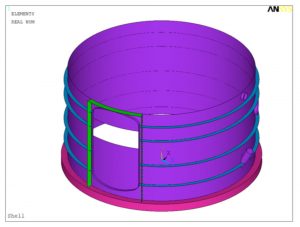
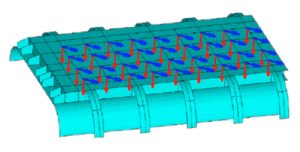
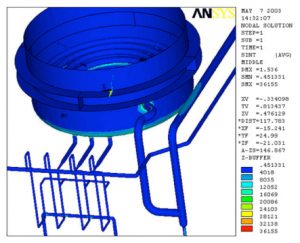
- Tank with Stiffening Rings
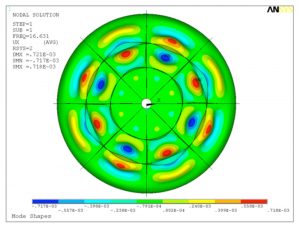
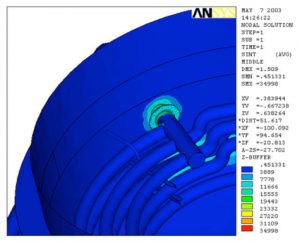
- Localized Buckling Mode Shapes
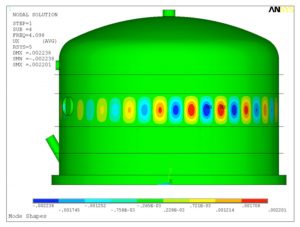
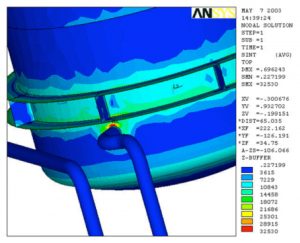
- Head with Stiffening Rings
- Localized Buckling Mode Shapes
Non-Linear Buckling Analysis of a Process Column
A non-linear Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was performed to determine the possibility of a local and/or global structural buckling instability in a process column under a partial vacuum of -1.5 psig. A local area, with various thin sections, was investigated for possible failure during the operation of the column. The resulting stress intensities, strain, and deformation were analyzed using the general intent of ASME Section VIII, Division 2 code.
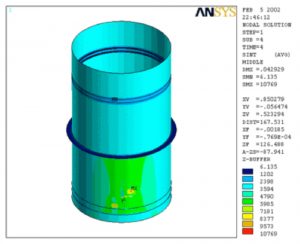
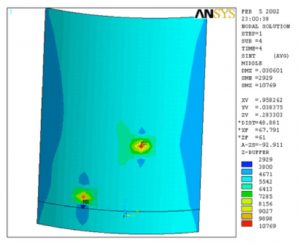
- Locations of Highest Stress in the Column Shell
- Locations of Highest Stress in the Column Shell
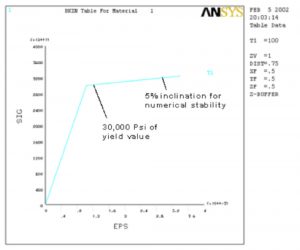
- True Stress/Strain Curve
Stress Analysis of a Furnace Stack Due to Over-Heating
The scope of this analysis was to perform thermal and structural analyses of the furnace under their operating conditions. A three dimensional Finite Element Model (FEM) of the furnace was constructed and analyzed to verify the stress levels. 2015 ASME Section VIII, Division 2, Part 5 was used as a guide to perform the analyses.
The thermal model included all the relevant components required for the complete thermal stress analysis. The convection coefficients were applied to the interior and exterior surfaces of the components. An initial analysis indicated the radiation effects were substantial compared to the convective heat transfer coefficients. Therefore, surface to ambient and surface to surface radiation phenomenon was also considered to achieve the desired temperatures on the cooling jacket as reported in the field data. The temperature distribution resulting from these thermal analyses were then used in the structural analysis as body loads. Structural Finite Element Analyses (FEA) was performed using the load combinations prescribed in ASME Section VIII, Division 2, Part 5 to determine the stresses in the vessel.
- General Layout of the Furnace
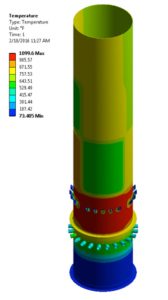
- Temperature Profile
- Residual Stress Distribution in the Furnace After Cooldown
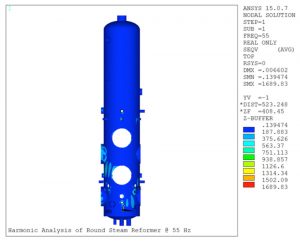
FEA Analysis of a Round Reformer with 4 Pulsating Gas Heaters
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was performed on a vertical reformer. Shell elements were used to model the reformer body and the attached nozzles. Static analysis was performed considering the operating pressure and temperature of the reformer, the usage of different thickness and material for construction. The effects of wind, seismic, and gravity loadings were also considered in the FEA. After determining the adequacy of the design, based on ASME Section VIII, Division 1 and Division 2, modal analyses were performed to determine the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the structure. Subsequently, harmonic analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of dynamic loads during the operation of the reformer. Coupled thermal-structural analysis was also performed to assess the effects of thermal stresses on the nozzles with high temperature gradients.
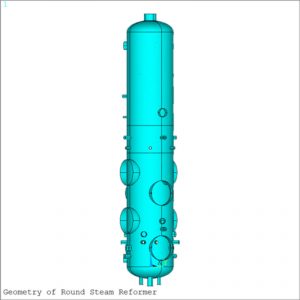
- Geometry of the vertical steam reformer – The Finite Element Model (FEM) is meshed using ANSYS 4 node “shell181” elements with 6 degrees of freedom at each node (3 rotational and 3 translational degrees of freedom).
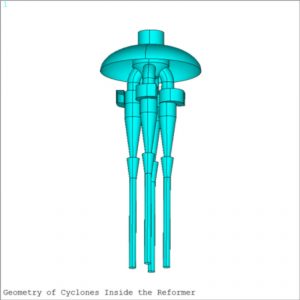
- Four cyclones were also considered in the FEM and connected to the inside of the top head.
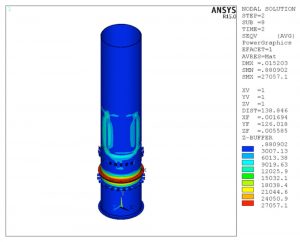
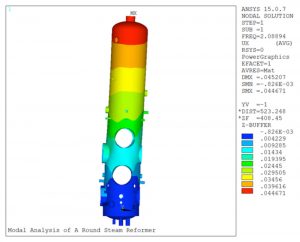
- Modal analysis was performed on the reformer considering a fixed support at the bottom tangent line. The natural frequencies of the first five mode shapes of the reformer were obtained from the analysis. The figure above illustrates the mode shape for the fundamental natural frequency of the reformer determined to be 3.80 Hz.
- The figure shows harmonic analysis performed on the round reformer at 55 Hz. The dynamic loads applied at this frequency range were related to the vibrations in the heaters. The maximum Von Mises stresses caused by these dynamic loads are observed around the heater elevations.
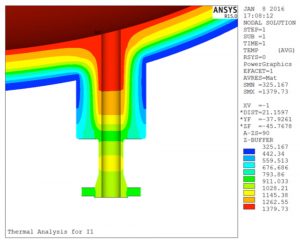
- The figure shows thermal analysis performed on one of the nozzles at the bottom of the reformer, which has an inside temperature of 1400°F. Based on the refractory setup inside the nozzle and reformer shell, and the conductivity properties of different materials in that location, the temperature decreases to approximately 350°F at the reformer-nozzle junction.
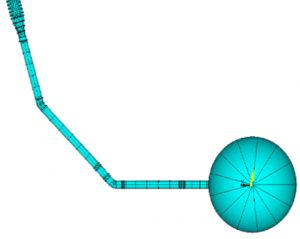
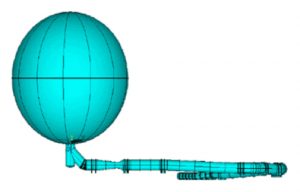
Nonlinear Buckling & Fatique Analysis of a Large Diameter Sphere & Its Complex Ductwork Under Transient External Pressure (MODEL)
In 2001, Openso Engineering was involved in a project with Northrop Grumman Space Technology (formerly TRW), U.S. Air Force, and Lockheed Martin for development of the YAL-1A Airborne Laser (ABL) system. Openso’s responsibility included performing nonlinear buckling and fatigue analysis of a large diameter sphere and its ductwork under transient external pressure. The sphere and ductwork were part of the recharging equipment for a modified Boeing 747 aircraft equipped with a chemical oxygen iodine laser.
- Top Down View of Chemical Oxygen Recharging Equipment
- Elevation View of Chemical Oxygen Recharging Equipment
- Ductwork for Chemical Oxygen Recharging Equipment
- Loads on the Ductwork for Chemical Oxygen Recharging Equipment
Failure Analysis of Flanges and Supports
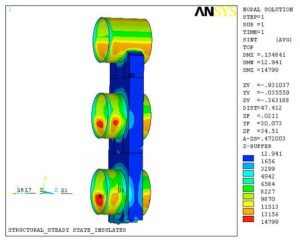
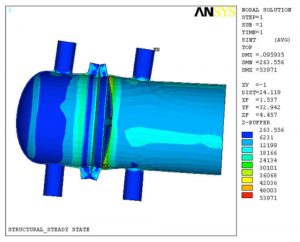
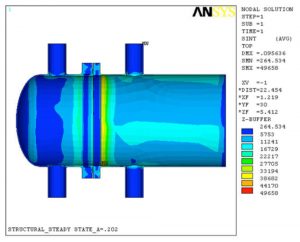
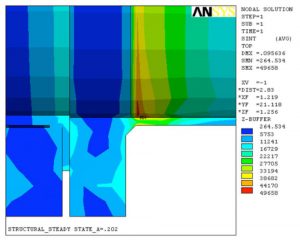
A Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was performed in support of a failure analysis of the cracks/failure of the flanges, supports, and fillet welds using brick elements. The Finite Element Model (FEM) consisted of nozzles, saddles, tube-sheets, body flanges, tubes, relevant tube side heads, shells, and inlet channels. A thermal stress analysis was performed to determine the state of stresses. The state of stresses was used in determination of the fatigue life of the area of concern.
- Geometry of the Finite Element Model
- Temperature Distribution of Heaters
- Stress Intensity Levels at the Supports
- Rotation of the Body Flange and Tube-sheet
- Enlarged view of the Rotation at Body Flange
- Stress Intensity in the Fillet Weld Connecting the Tube-sheet and Shell
- Enlarged View of the Fillet Weld Connecting the Tube-sheet and Shell
Finite Element Analysis/Fatigue Analysis of Three Vessels Interconnected With a Complex Piping System
A 3D Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was performed for three vessels, their internal coils, and their interconnecting piping systems. The operating condition of the reactors includes the effects of the internal vessel pressure, internal coil pressure, thermal gradients, agitation loads, and gravity forces.
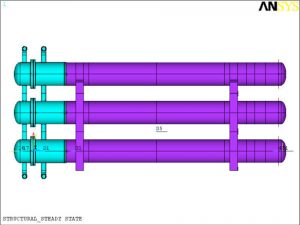
- Plan View of Three Vessels with Piping Attached
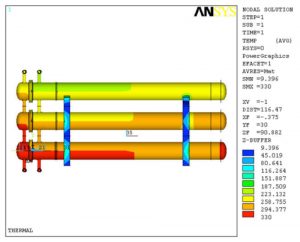
- Stresses of Pipe Nozzle Attachment to Shell Wall
- Stresses of Pipe Nozzle Attachment to Shell Wall
- Stresses of Pipe Nozzle Attachment to Shell Wall
Design and Analysis of New Dryer Scrubber
The scope of this project was to design and analyze a New Dryer Scrubber with the following design conditions: atmospheric pressure -35” of water column partial vacuum at 230ºF plus max liquid level of 4’-8”. The tank and nozzles of the Scrubber were designed per API 650. The preliminary tank design was based on longhand calculations, and then analyzed using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to verify the adequacy of the tank under the design conditions (nozzle loads and wind/seismic loads were provided by the customer).
- von Mises Stresses at the Outlet Nozzle on the Tank Roof. Max Stress Occurs at the Junction of the Web Plate and the Nozzle Neck.
- von Mises Stresses at the Inlet Nozzle on the Tank Wall. Max Stress Occurs at the Junction of the Nozzle Neck and the Tank Wall.
- Maximum Displacements can be Seen at the tip of Outlet Nozzle on the Roof and Midway up the Tank Wall.
- Replacement Scrubber Tank per API 650
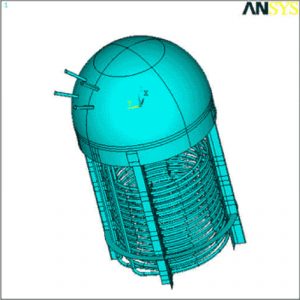
Finite Element Analysis/Fatigue Analysis of Reactor and its Internal Coils
A 3D Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was performed for the top head and internals of a reactor. The operating condition of the reactor included the effects of internal pressure, temperature gradients, agitation loads, and gravity forces.
- Layout of the dome and Internal Coils
- Layout of the dome and Internal Coils
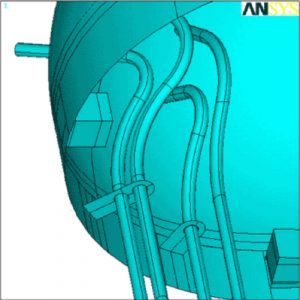
- Layout of the Internal Coils and Piping
- Layout of the Internal Coils and Piping
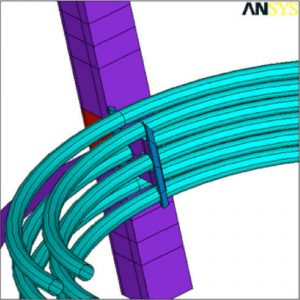
- Stress on Coil to Dome Penetration
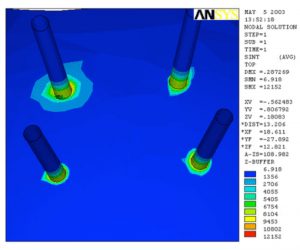
- Stress on Internal Coil Support
- Layout of the dome and Internal Coils